JavaScript中一些较常用, 能提高效率的数组方法.
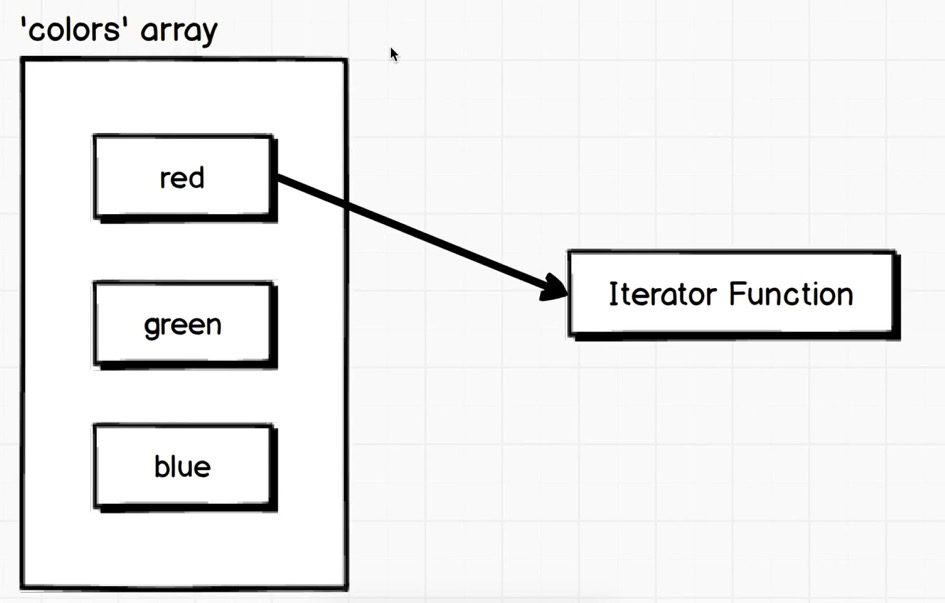
forEach 示例:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 const colors = ['red' , 'green' , 'blue' ];for (var i = 0 ; i < colors.length; i++){ console .log(colors[i]); } colors.forEach(color => console .log(color); });
原数组的元素被遍历传入Iterator Function并执行.
更实际的应用:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 const numbers = [1 , 2 , 3 , 4 ];let sum = 0 ;numbers.forEach(number => sum += number; }); console .log(sum);
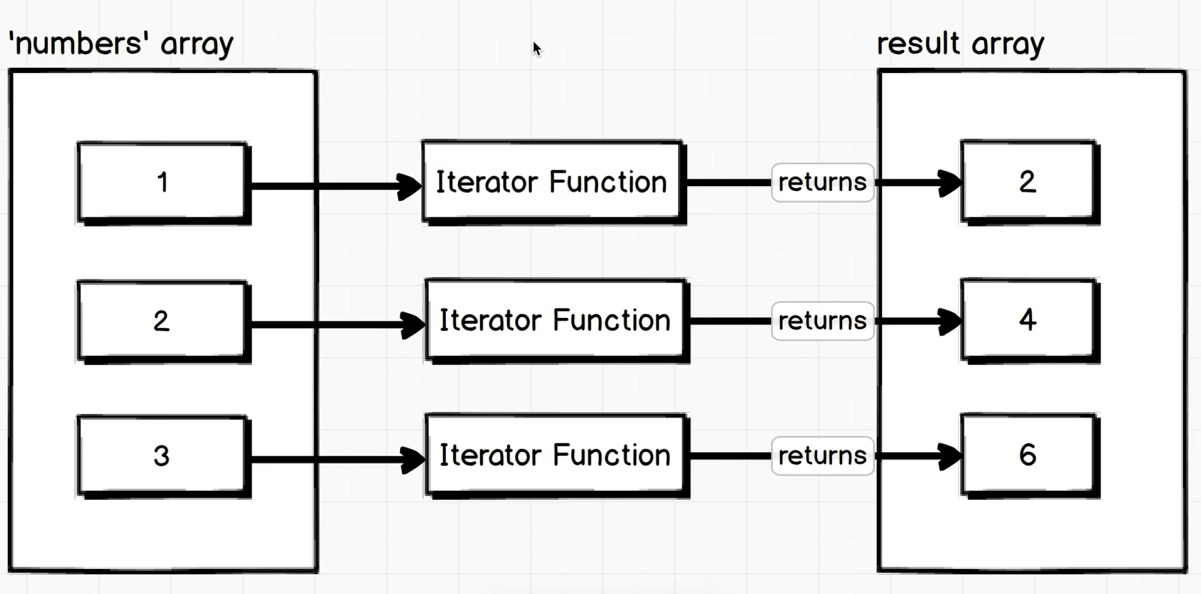
map 示例:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 const numbers = [1 , 2 , 3 , 4 ];let doubledNumbers = []; for (var i = 0 ; i < numbers.length; i++){ doubledNumbers.push(numbers[i] * 2 ) } console .log(doubledNumbers); let doubledMap = numbers.map(number =>2 )console .log(doubledMap);
原数组的元素被遍历传入Iterator Function并执行, 执行后的结果被返回并存入新数组.
map可以用于汇总数组内各个元素的属性值, 并输出相关信息. 例子:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 const cars = [ {model : 'Buick' , price : 'cheap' }, {model : 'Camaro' , price : 'expensive' } ]; const model = cars.map(car => return car.model; }); console .log(model); const price = cars.map(car => return car.price; }); console .log(price);
渲染数据列表:
可在浏览器控制台输入以下代码片段查看效果
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 const cars = [ {model : 'Buick' , price : 'cheap' }, {model : 'Camaro' , price : 'expensive' } ]; const carsList = document .createElement('ul' ); const aboutCars = cars.map(car => return `<li>${car.model} is ${car.price} </li>` ; }); aboutCars.forEach(car => carsList.innerHTML += car; }) document .body.innerHTML = '' ;document .body.appendChild(carsList);
更实际的应用:
filter 示例:
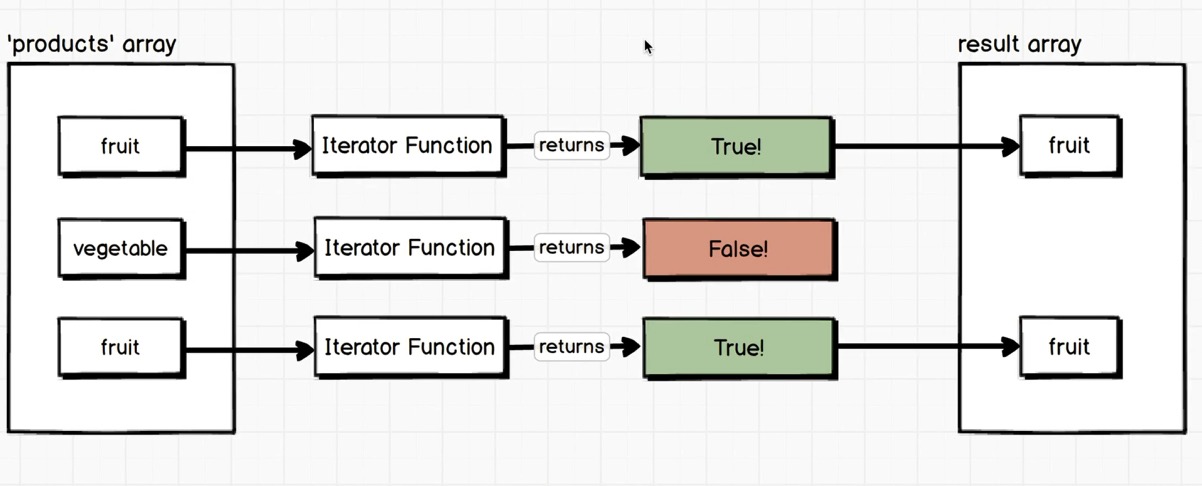
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 const products = [ { name : 'cucumber' , type : 'vegetable' , quantity : 10 , price : 1 }, { name : 'banana' , type : 'fruit' , quantity : 8 , price : 15 }, { name : 'cucumber' , type : 'vegetable' , quantity : 25 , price : 12 }, { name : 'orange' , type : 'fruit' , quantity : 30 , price : 8 }, ] let filteredProducts = [];for (var i = 0 ; i < products.length; i++){ if (products[i].type === 'fruit' ){ filteredProducts.push(products[i]) } } console .table(filteredProducts);const fruit = products.filter(product =>'fruit' );console .table(fruit);const veg = products.filter(product =>'vegetable' && product.quantity > 0 && product.price < 10 );console .table(veg);
console.table将数组以表格的形式显示在控制台中, 可读性更强.
原数组的元素被遍历传入Iterator Function, Iterator Function返回值的类型为布尔值, 如果返回true, 则该元素被存入结果数组.
更实际的应用:
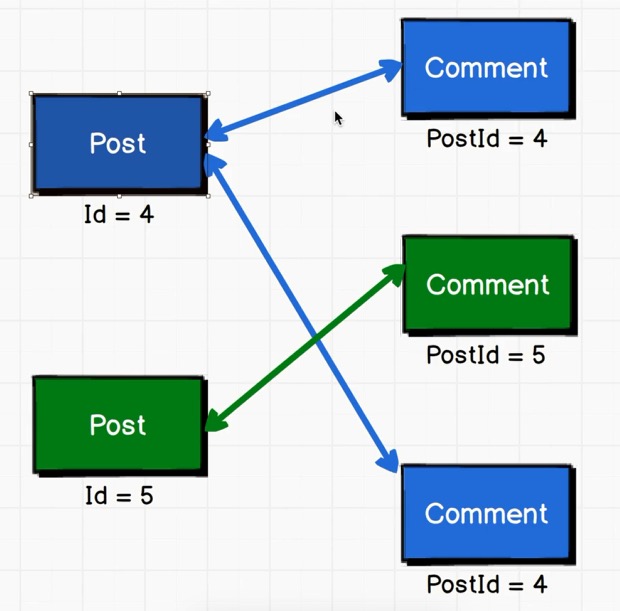
筛选出指定post的comment内容:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 const post = { id : 4 , title : 'New Post' };const comments = [ { postId : 4 , content : 'Awesome Post' }, { postId : 3 , content : 'It was ok' }, { postId : 4 , content : 'neat' } ]; function commentsForPost (post, comments ) return comments.filter(comment => } const filteredComments = commentsForPost(post, comments);console .table(filteredComments);
在Todo App中:
未完成的todo会一直显示, 完成的todo只有在showCompleted为true时才显示1 2 3 const filteredTodos = filteredTodos.filter((todo ) => { return !todo.completed || showCompleted; });
Ps: 逻辑操作符 ||(“或”)
expr1 || expr2, 如果表达式结果为true, 则返回expr1, false则返回expr1, 因此当参数为布尔值时, 任意一个参数为true, expr1 || expr2返回的结果就为true.
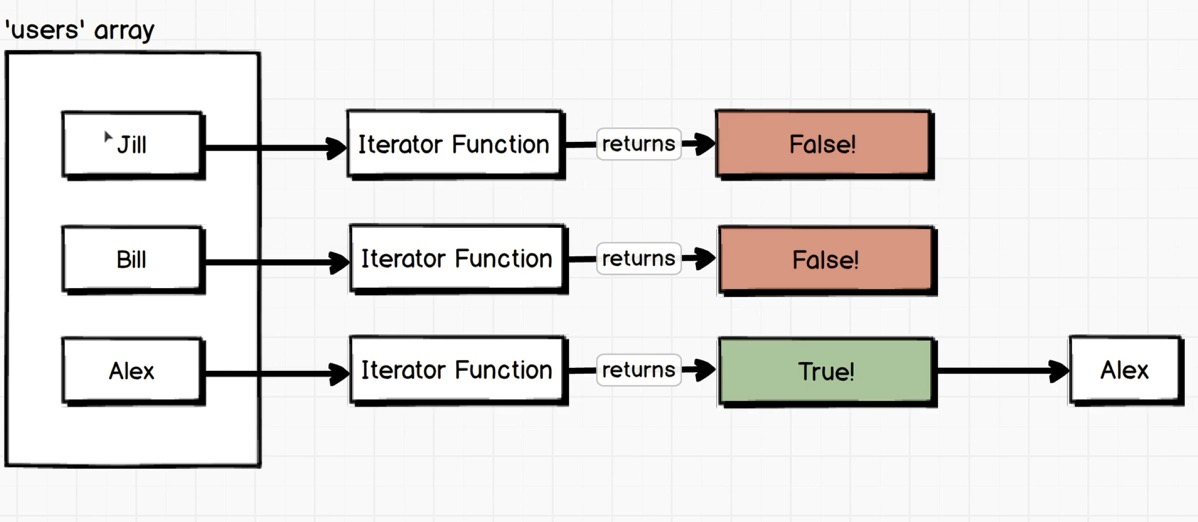
find and findIndex 示例:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 const users = [ {name : 'Jill' }, {name : 'Bill' }, {name : 'Alex' } ]; let user;for (var i = 0 ; i < users.length; i++){ if (users[i].name === 'Alex' ){ user = users[i]; break ; } } console .log(user); const findUser = users.find(user =>'Alex' );console .log(findUser);
原数组的元素被按顺序被传入Iterator Function, Iterator Function返回值的类型为布尔值, 当Iterator Function返回true时, 停止调用Iterator Function, 并返回停止前最后一个Iterator Function执行的结果.
如果有两个相同的元素符合要求, 只有第一个会被返回.
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 function Car (model ) this .model = model; } const cars = [ new Car('Buick' ), new Car('Camaro' ), new Car('Focus' ) ]; const focusCar = cars.find(car =>'Focus' )console .log(focusCar);
更实际的应用:
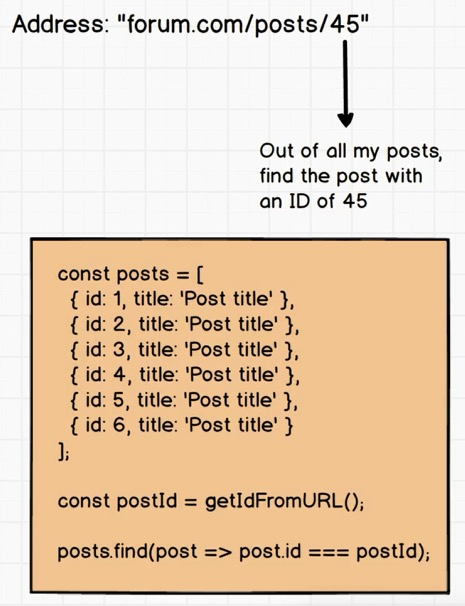
利用find寻找特定id值的post:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 const posts = [ { id : 1 , title : 'New Post' }, { id : 2 , title : 'Old Post' } ] const comment = { postId : 1 , content : 'Awesome Post' };function postForComment (posts, comment ) return posts.find(post => } postForComment(posts, comment);
删除特定评论:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 const comments = [ { text : 'Love this!' , id : 523423 }, { text : 'Super good' , id : 823423 }, { text : 'You are the best' , id : 2039842 }, { text : 'Ramen is my fav food ever' , id : 123523 }, { text : 'Nice Nice Nice!' , id : 542328 } ]; const comment = comments.find(comment =>823423 );console .log(comment);const commentIndex = comments.findIndex(comment =>823423 );console .log(commentIndex); const newComments = [ ...comments.slice(0 , commentIndex), ...comments.slice(commentIndex + 1 ) ]; console .table(comments);console .table(newComments);
every and some 示例:
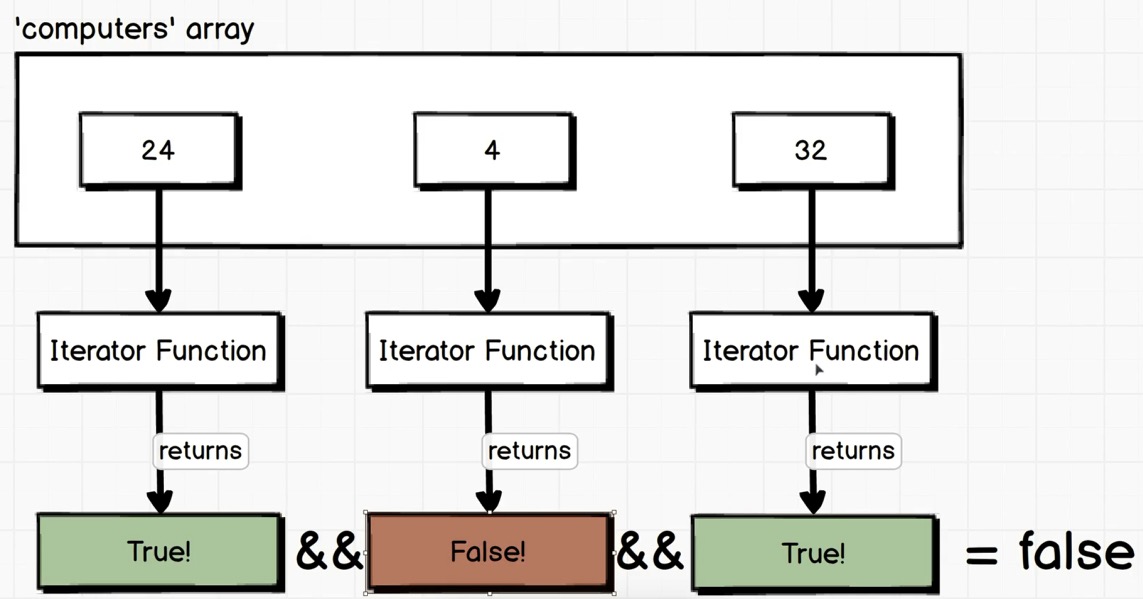
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 const computers = [ {name : 'Apple' , ram : 24 }, {name : 'Compaq' , ram : 4 }, {name : 'Acer' , ram : 32 } ]; let allComputersCanRunProgram = true ;let onlySomeComputersCanRunProgram = false ;for (let i = 0 ; i < computers.length; i++){ let computer = computers[i]; if (computer.ram < 16 ) { allComputersCanRunProgram = false ; } else { onlySomeComputersCanRunProgram = true ; } } console .log(allComputersCanRunProgram); console .log(onlySomeComputersCanRunProgram); const allComputers = computers.every(computer =>16 );console .log(allComputers); const onlySomeComputers = computers.some(computer =>16 );console .log(onlySomeComputers);
every:
数组元素被遍历传入Iterator Function, Iterator Function返回布尔值.
返回布尔值后, 会检视所有值并通过逻辑操作符&&(与)对最后结果进行判断.
如果每一个函数所返回的布尔值是true, 那么最后结果就为true, 有一个为false, 最后结果就为false.
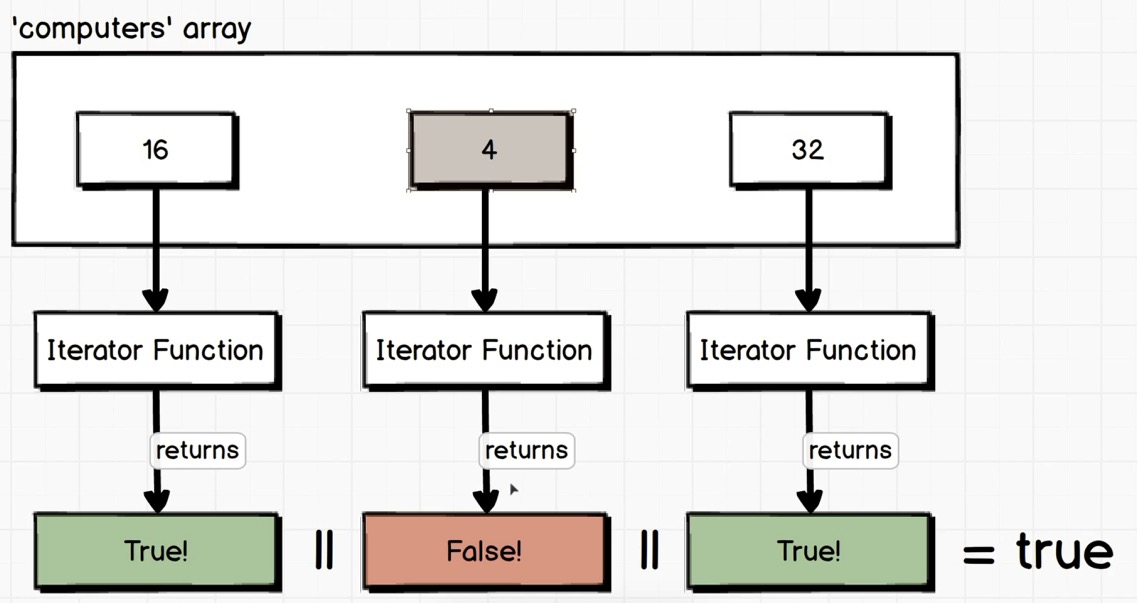
some:
some与every很相似:
数组元素被遍历传入Iterator Function, Iterator Function返回布尔值.
返回布尔值后, 会检视所有值并通过逻辑操作符||(或)对最后结果进行判断.
如果每一个函数所返回的布尔值中有一个为true, 那么最后结果就为true, 全部为false, 最后则是false.
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 const people = [ { name : 'Wes' , year : 1988 }, { name : 'Kait' , year : 1986 }, { name : 'Irv' , year : 1970 }, { name : 'Lux' , year : 2015 } ]; const isAdult = people.some(person =>new Date ()).getFullYear()) - person.year >= 19 );console .log(isAdult);console .log({isAdult}); const allAdult = people.every(person =>new Date ()).getFullYear()) - person.year >= 19 );console .log({allAdult});
更实际的应用:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 function Field (value ) this .value = value; } Field.prototype.validate = function ( return this .value.length > 0 ; } let username = new Field('2cool' );let password = new Field('my_password' );let birthdate = new Field('10/10/2010' );username.validate() && password.validate() && birthdate.validate() let fields = [username, password, birthdate];let formIsValid = fields.every(field =>if (formIsValid) { }else { }
sort 1 2 3 4 5 6 function compareFunction (a, b ) } arr.sort(compareFunction);
示例:
1 2 3 4 5 var numbers = [4 , 20 , 5 , 1 , 3 ];numbers.sort(function (a, b ) return a - b; }); console .log(numbers);
如果没有comparisonFunction, 先将数列中的内容转化成字符串再根据Unicode顺序排序.
1 2 3 4 5 var scores = [1 , 10 , 21 , 2 ];scores.sort(); console .log(scores);
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 const inventors = [ { first : 'Albert' , last : 'Einstein' , year : 1879 , passed : 1955 }, { first : 'Isaac' , last : 'Newton' , year : 1643 , passed : 1727 }, { first : 'Galileo' , last : 'Galilei' , year : 1564 , passed : 1642 }, { first : 'Marie' , last : 'Curie' , year : 1867 , passed : 1934 }, { first : 'Johannes' , last : 'Kepler' , year : 1571 , passed : 1630 }, { first : 'Nicolaus' , last : 'Copernicus' , year : 1473 , passed : 1543 } ]; inventors.sort((a, b ) => a.year - b.year ? 1 : -1 ); console .table(inventors);inventors.sort((a, b ) => { return (a.passed - a.year) - (b.passed - b.year); }); console .table(inventors);
对数组以元素字母顺序进行排序
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 const people = ['Beck, Glenn' , 'Becker, Carl' , 'Beckett, Samuel' , 'Beddoes, Mick' , 'Beecher, Henry' , 'Billings, Josh' , 'Biondo, Frank' , 'Birrell, Augustine' , 'Black, Elk' , 'Blair, Robert' , 'Blair, Tony' , 'Blake, William' ]const alpha = people.sort((lastOne, nextOne ) => { const [aLast, aFirst] = lastOne.split(', ' ); const [bLast, bFirst] = nextOne.split(', ' ); return aLast > bLast ? 1 : -1 ; }) console .log(alpha);
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 const bands = ['The Plot in You' , 'The Devil Wears Prada' , 'Pierce the Veil' , 'Norma Jean' , 'The Bled' , 'Say Anything' , 'The Midway State' , 'We Came as Romans' , 'Counterparts' , 'Oh, Sleeper' , 'A Skylit Drive' , 'Anywhere But Here' , 'An Old Dog' ];function strip (bandName ) return bandName.replace(/^(a |the |an )/i , '' ).trim(); }; const sortedBands = bands.sort((a,b ) => strip(a) > strip(b) ? 1 : -1 );console .log(sortedBands);
Todo App中, 未完成的Todo显示在已完成的之前:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 let sortedTodos;sortedTodos.sort((a, b ) => { if (!a.completed && b.completed){ return -1 ; }else if (a.completed && !b.completed) { return 1 ; }else { return 0 ; } })
Ps: 逻辑操作符 &&(“与”)
expr1 && expr2, 如果表达式结果为false, 则返回expr1, 否则返回expr2, 因此当参数为布尔值时, 若参数均为true, 则结果返回true, 否则返回false.
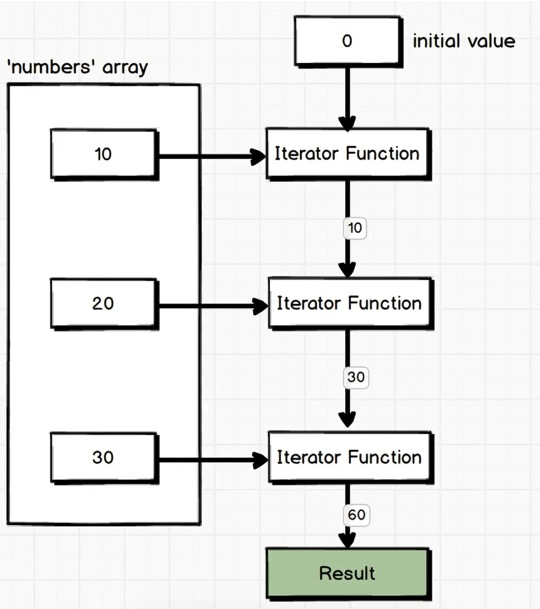
reduce 示例:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 const numbers = [10 ,20 ,30 ];let sum = 0 ;for (var i = 0 ; i < numbers.length; i++){ sum += numbers[i]; } console .log(sum); const reduceSum = numbers.reduce((sum, number )=> { return sum + number; }, 0 ); console .log(reduceSum);
传入reduce的第二个参数是初始值(initial value), 第一个参数是Iterator Function, Iterator Function接受两个参数, 第一次执行接受初始值和原数组中的第一个元素作为参数, 执行结束后返回的值作为Iterator Function的第一个参数, 原数组中的第二个元素作为第二个参数, 以此类推.
reduce功能强大, 可以使用reduce实现以上所有数组方法的功能.
reduce实现map的功能:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 let primaryColors = [ {color : 'red' }, {color : 'yellow' }, {color : 'blue' }, ]; const reducedColor = primaryColors.reduce((accumulator, primaryColor )=> { accumulator.push(primaryColor.color); return accumulator; }, []); console .log(reducedColor); const mappedColor = primaryColors.map(primaryColor =>console .log(mappedColor);
计算order总量 :
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 const orders = [ { amount : 250 }, { amount : 200 }, { amount : 340 }, { amount : 100 } ] let totalAmount = orders.reduce((sum, order ) => { return sum + order.amount }, 0 ); console .log(totalAmount);
计算各个交通工具的个数
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 const data = ['car' , 'car' , 'truck' , 'truck' , 'bike' , 'walk' , 'car' , 'van' , 'bike' , 'walk' , 'car' , 'van' , 'car' , 'truck' ];const transportation = data.reduce((obj, item ) => { if (!obj[item]) { obj[item] = 0 ; } obj[item]++; return obj; }, {}); console .log(transportation);
检查括号是否对称
(必须是一对括号且左括号在前) [balanced parentheses]:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 function balancedParens (string ) return !string.split('' ).reduce(function (counter, char ) if (counter < 0 ) {return counter;} if (char === "(" ) {return ++counter;} if (char === ")" ) {return --counter;} return counter; },0 ); } balancedParens("((())))" ); balancedParens("))((()" ); balancedParens("(((())))" ); balancedParens("()()()()" ); balancedParens('()()()skoaksod' );
string.split(''): 因为reduce只能在数组中使用, 所以先将参数的类型从string转化为array;将初始值设为0, 若数组中出现(, 计数器(counter)+1, 出现)计数器减1, 只有当计数器最后结果为0时返回true;
!会将结果强制转换(coercion)为布尔值;if (counter < 0) {return counter;}: 如果计数器值为负, 直接返回, 最后结果就为false, 因为左括号必须在右括号之前.
计算下例中视频时间总和
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 <ul class ="videos" > <li data-time ="5:43" > Video 1</li > <li data-time ="2:33" > Video 2</li > <li data-time ="3:45" > Video 3</li > <li data-time ="0:47" > Video 4</li > <li data-time ="5:21" > Video 5</li > <li data-time ="6:56" > Video 6</li > <li data-time ="3:46" > Video 7</li > <li data-time ="5:25" > Video 8</li > <li data-time ="3:14" > Video 9</li > <li data-time ="3:31" > Video 10</li > </ul >
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 const timeNodes = [...document.querySelectorAll('[data-time]' )];const seconds = timeNodes .map(node => .map(timeCode => const [mins, secs] = timeCode.split(':' ).map(parseFloat ); return (mins * 60 ) + secs; }) .reduce((total, vidSeconds ) => total + vidSeconds); let secondsLeft = seconds;const hours = Math .floor(secondsLeft / 3600 );secondsLeft = secondsLeft % 3600 ; const mins = Math .floor(secondsLeft / 60 );secondsLeft = secondsLeft % 60 ; console .log(hours, mins, secondsLeft);
参考